Five basic rules of database structure
- Order doesn’t matter
- No duplicate rows
- Every cell contains one value
- One column per type of information
- No redundant information
1. Order doesn’t matter
- The information should not be dependent on the order of the rows or the order
of the columns
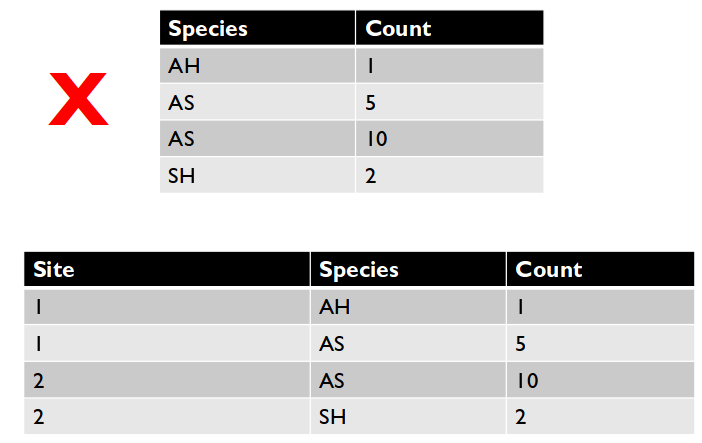
2. No duplicate rows
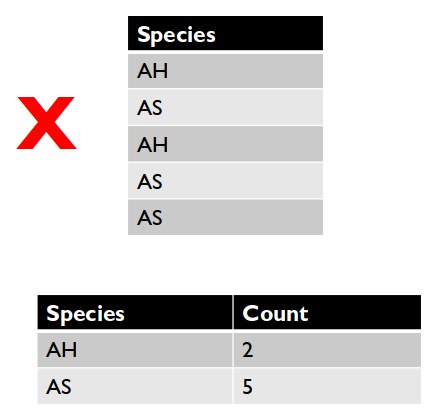
3. Every cell contains one value
- This is an example of what not to do.
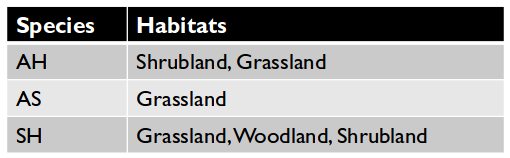
- How would you query for
'Shrubland'?
- This is also an example of what not to do.
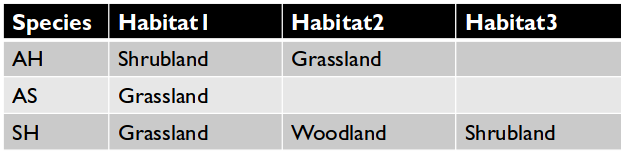
- How would you query for records with
'Grassland' AND 'Shrubland'?
Restructure the examples of what not to do for #3 and #4.
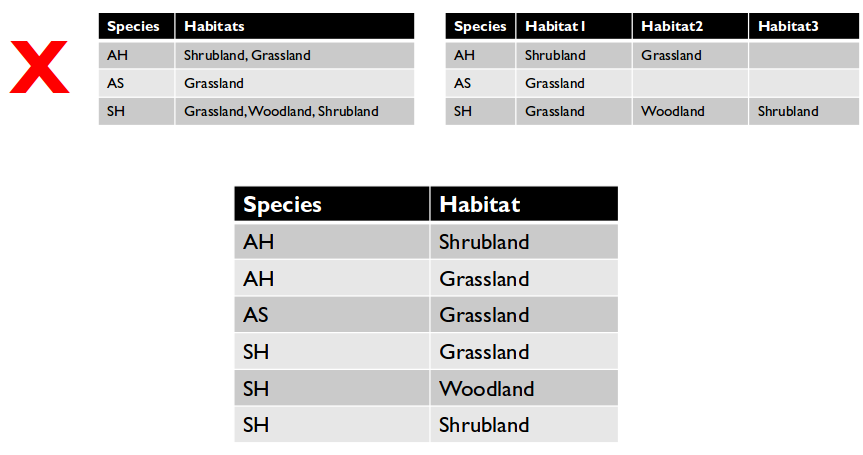
- The proper structure lets us easily subset the data however we want.
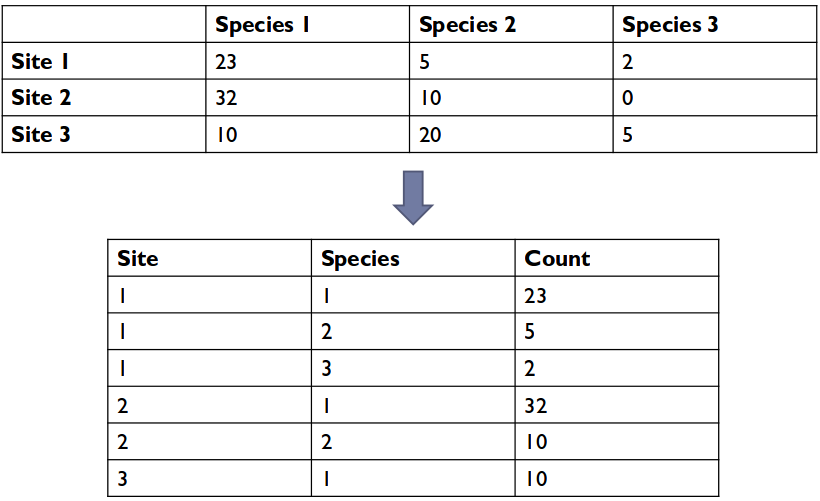
Cross-tablulated data is difficult for SQL to work with.
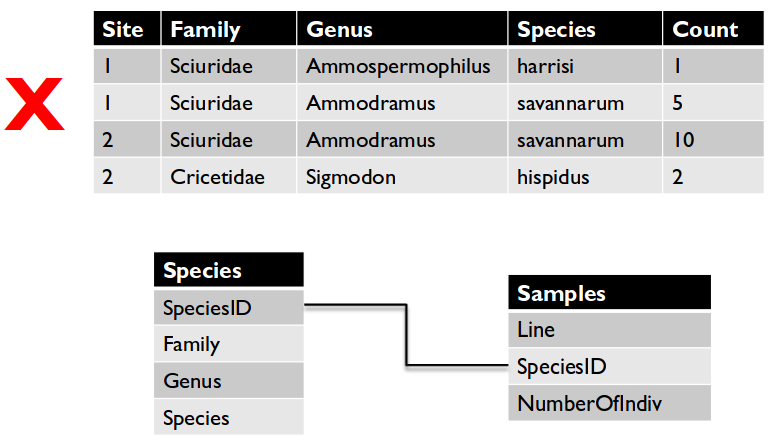
- Redundant information makes it more difficult to update or revise data.
- If something changes we want to be able to change it in one place, not hundreds of places.
- Use multiple tables to avoid redundant information.
- Easier and less error prone
- Use a Unique
RecordID to link tables with complementary information.
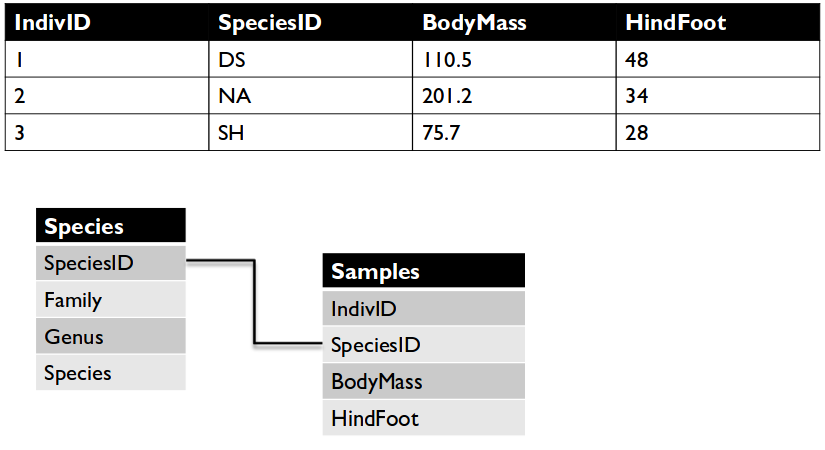
Multiple tables
- It is often not efficient to include all information of interest in a single
table.
- To solve these problems,
- store data in multiple tables, and
- connect the data in different tables using
JOIN to describe
relationships between tables (hence “relational” database)
- Each table contains a single data type